How to Easily Add 30 Different Plants to Your Diet Each Week for Better Gut Health
"A healthy gut microbiome is a diverse gut microbiome"
Incorporating a diverse array of plant-based foods into your diet is a powerful strategy for enhancing gut health and overall well-being. Research from the American Gut Project indicates that individuals who consume more than 30 different plant types weekly have a more diverse gut microbiome compared to those who consume fewer than 10.
A diverse microbiome is associated with improved digestion, stronger immunity, and a reduced risk of chronic diseases.
To help you get started, we’ve created a plant-diverse recipe below that’s packed with a variety of vibrant, nutrient-rich ingredients. It’s a delicious and simple way to boost your plant intake and support your overall health. Dive in and discover how easy it can be to nourish your body with the power of plants!
Strategies to Achieve 30 Different Plants Per Week:
Diversify Your Grains: Instead of sticking to just rice or wheat, explore grains like quinoa, barley, millet, and farro. Each offers unique nutrients and contributes to your plant variety count.
Embrace Legumes: Incorporate beans, lentils, chickpeas, and peas into your meals. They are excellent sources of protein and fiber, and each type adds to your plant diversity.
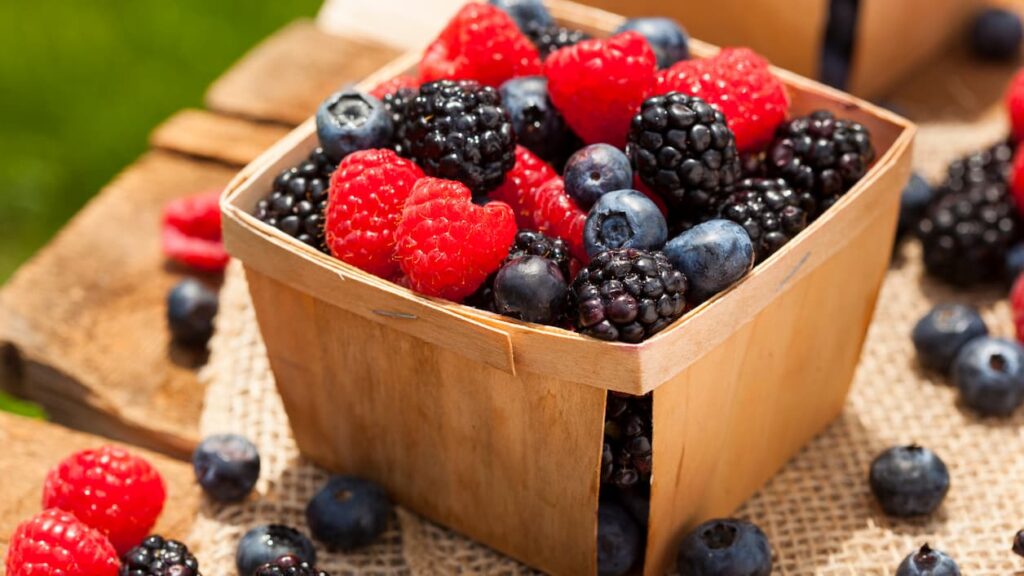
Rotate Vegetables and Fruits: Aim to include a colorful mix of vegetables and fruits daily. For example, add spinach, bell peppers, carrots, and tomatoes to your salads, and enjoy fruits like berries, apples, and citrus as snacks.
Incorporate Nuts and Seeds: Sprinkle chia seeds, flaxseeds, sunflower seeds, almonds, and walnuts onto your cereals, yogurts, or salads. These not only boost plant variety but also provide healthy fats.
Use Herbs and Spices: Fresh herbs like basil, cilantro, parsley, and spices such as turmeric, cumin, and coriander can enhance flavor and contribute to your plant count.
Try Fermented Foods: Foods like sauerkraut, kimchi, and tempeh are not only diverse plant sources but also support gut health through beneficial probiotics.
Practical Tips:
Meal Planning: Plan your meals to include a variety of plant-based ingredients. For instance, a stir-fry can incorporate multiple vegetables, tofu, and a sprinkle of sesame seeds.
Batch Cooking: Prepare dishes like vegetable soups, stews, or grain salads in bulk, using different plant ingredients. This ensures you have diverse, ready-to-eat meals throughout the week.
Explore New Recipes: Challenge yourself to try new plant-based recipes that introduce different ingredients. This keeps your meals exciting and varied.

Why Does Diversity Matter?
Your gut microbiome consists of trillions of bacteria, each playing a role in keeping your body functioning optimally. These bacteria thrive on different types of dietary fibers found in various plant-based foods. By consuming a diverse diet, you ensure that these beneficial bacteria have the nutrients they need to thrive and multiply. A richer and more diverse microbiome can better support your overall well-being, reduce inflammation, and improve your body’s resilience to diseases.
Benefits Beyond the Gut
A diverse diet doesn’t just support gut health; it can have a ripple effect on your overall well-being. People with a healthy, diverse microbiome often experience better mental clarity, improved energy levels, and a greater sense of well-being. Additionally, eating a variety of plants helps you get a broader spectrum of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, all of which contribute to a stronger and more resilient body.
By consciously making an effort to incorporate a wider range of plant-based foods into your diet, you are investing in your health and future. So, get creative in the kitchen, try new flavors, and enjoy the journey of nourishing your body with the power of plants!
🎥 Ready to elevate your plant-based cooking game? 🌱 Subscribe to our YouTube channel now for exclusive tutorials, chef-led masterclasses, and creative recipes that will inspire every meal. Don’t miss out—hit that subscribe button today! 🙌

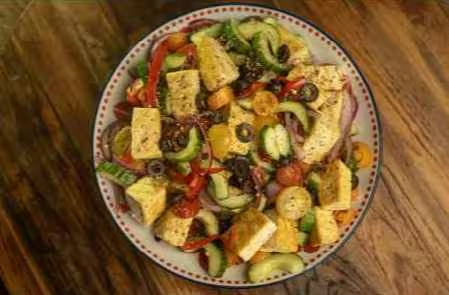



Responses